Interactive Penguin Tracking
All Migrating Penguins
Tracking Migration of Magellanic Penguins
Thanks to the generous funding by Zoo Augsburg in Germany, Katie Holt and Eric Wagner traveled to Punta Tombo, Argentina in April 2024. They attached satellite-tracking tags to 20 Magellanic penguins for their fall migration (10 females and 10 males), to supplement the migration data from previous trips and investigate interannual variation in migratory behavior.
The overall goal of the study is to determine where penguins spend the austral fall and winter, and where they might come into conflict with fishing, shipping, or pollution. Former Center postdoctoral researcher Tasha Gownaris showed that more females than males die at sea during the winter. Learning whether females and males migrate to the same locations can help us understand why, and help inform policies to protect the females.
We invite you to explore the interactive maps on this page by clicking on any one of the penguins’ names on the maps.
2022-2023 Migration Comparison
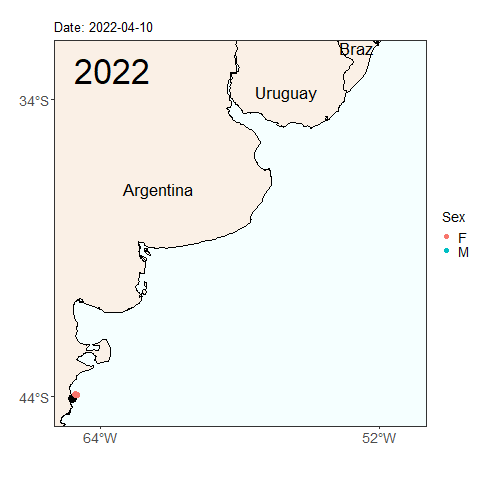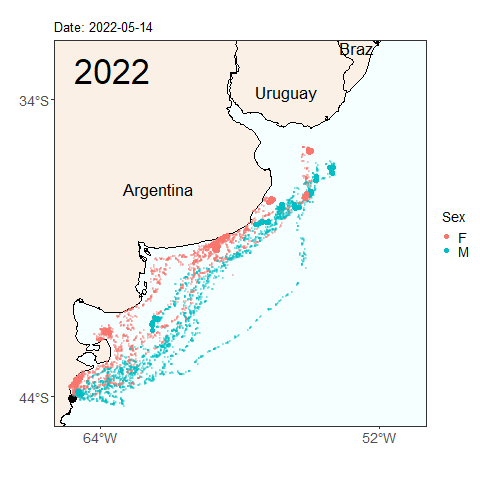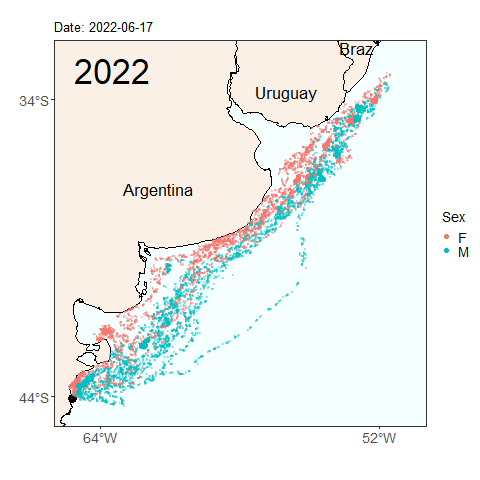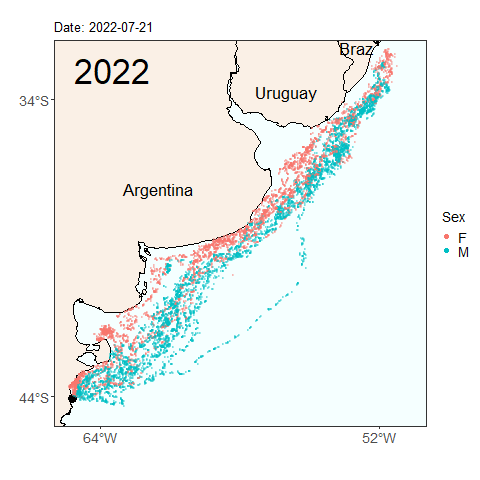
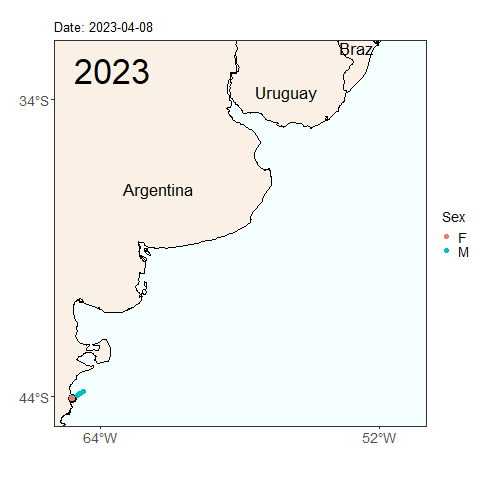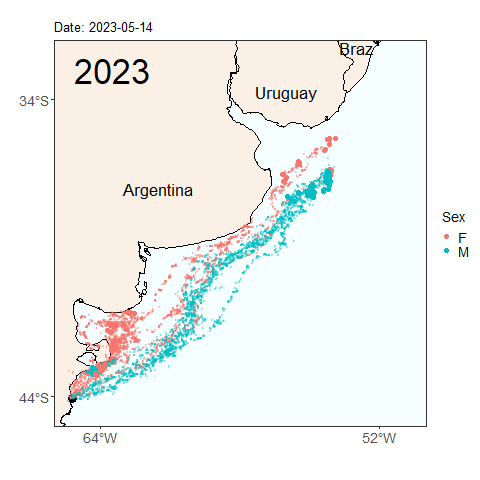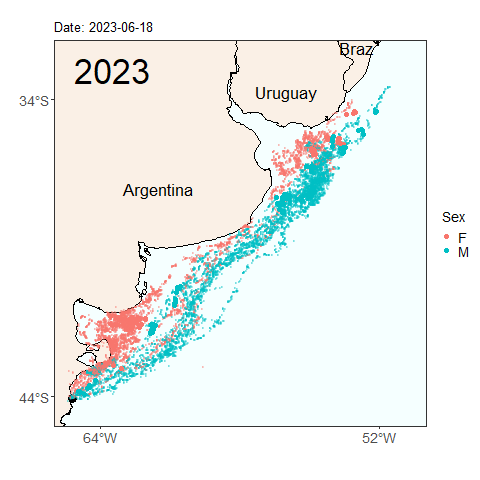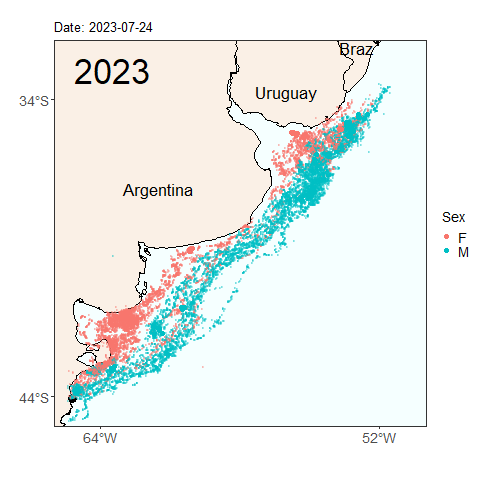
Here we see the migration tracks from 2022 and 2023 within the same time period of early April to July 24. Notice how the penguins swam further north within the same time period last year than they did this year. Do you see any other differences between the years?
Will this year’s penguins reach the same latitude as the penguins from last year by the end of the migratory season? Was last year’s longer migration typical, or atypical? These are the types of questions we can start to answer by continuing our long term monitoring study of penguins. Help us continue our studies by donating to the Center for Ecosystem Sentinels.